개발자입니다
[비트캠프] 61일차(13주차3일) - Java(네트워킹), myapp-29~32 본문
29. CSV 텍스트 형식으로 출력하기 : FileReader / FileWriter
### 29. 인스턴스를 CSV 텍스트 형식으로 입출력하기: FileReader/FileWriter
- 객체의 필드 값을 텍스트로 입출력하는 방법
- CSV 형식으로 한 객체의 필드 값을 한 줄 단위로 출력하는 방법

FileOutputStream 의 write( 정수 ) 에 '가' 를 입력하면 0xac00 (UTF-16) 으로 변환한다. 맨 끝 1byte를 있는 그대로 출력하므로 00 으로 출력한다.
FileWriter 의 write( 문자코드) 에 '가' 를 입력하면 0xac00 (UTF-16) 으로 변환한다. 'A' 를 입력하면 0x0041 로 변환한다. 이유는 JVM 옵션인 file.encoding 에 지정된 문자집합의 코드로 변환하기 때문이다. '가' 는 eab080 으로, 'A' 는 41 로 출력한다.
JVM 에서 문자(char) 는 2byte 로 UTF-16 이다.
29. 텍스트 출력 / 입력

객체를 CSV 형식 텍스트인 "값,값,값,값,..." 으로 바꾼다. FileWriter 의 write() 를 이용해 UTF-8 문자 코드표에 따라 텍스트 파일로 변환한다.
FileReader의 read() 로 텍스트 파일에서 UTF-8 문자 코드를 읽는다. 이를 UTF-16 문자코드로 변환한다. BufferedReader 이용하여 한 줄의 문자열인 "값,값,값,값,..." 로 바꾸고 이를 객체의 필드에 저장한다.
BufferedReader 를 Decorator 라 한다.
package bitcamp.myapp.dao;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class BoardDao {
/* 아래 코드 수정 */
public void save(String filename) {
try (FileWriter out = new FileWriter(filename)) {
list.forEach(b -> {
try {
out.write(String.format("%d,%s,%s,%s,%d,%s\n",
b.getNo(),
b.getTitle(),
b.getContent(),
b.getPassword(),
b.getViewCount(),
b.getCreatedDate()));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("데이터 출력 중 오류 발생!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void load(String filename) {
if (list.size() > 0) { // 중복 로딩 방지!
return;
}
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))) {
while (true) {
String str = in.readLine();
if (str == null) {
break;
}
String[] values = str.split(",");
Board b = new Board();
b.setNo(Integer.parseInt(values[0]));
b.setTitle(values[1]);
b.setContent(values[2]);
b.setPassword(values[3]);
b.setViewCount(Integer.parseInt(values[4]));
b.setCreatedDate(values[5]);
list.add(b);
}
if (list.size() > 0) {
lastNo = list.get(list.size() - 1).getNo();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package bitcamp.myapp.dao;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class TeacherDao {
/* 아래 코드 수정 */
public void save(String filename) {
try (FileWriter out = new FileWriter(filename)) {
list.forEach(obj -> {
try {
out.write(String.format("%d,%s,%s,%s,%s,%d,%s,%s,%d\n",
obj.getNo(),
obj.getName(),
obj.getTel(),
obj.getCreatedDate(),
obj.getEmail(),
obj.getDegree(),
obj.getSchool(),
obj.getMajor(),
obj.getWage()));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("데이터 출력 중 오류 발생!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void load(String filename) {
if (list.size() > 0) { // 중복 로딩 방지!
return;
}
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))) {
while (true) {
String str = in.readLine();
if (str == null) {
break;
}
String[] values = str.split(",");
Teacher obj = new Teacher();
obj.setNo(Integer.parseInt(values[0]));
obj.setName(values[1]);
obj.setTel(values[2]);
obj.setCreatedDate(values[3]);
obj.setEmail(values[4]);
obj.setDegree(Integer.parseInt(values[5]));
obj.setSchool(values[6]);
obj.setMajor(values[7]);
obj.setWage(Integer.parseInt(values[8]));
list.add(obj);
}
if (list.size() > 0) {
lastNo = list.get(list.size() - 1).getNo();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package bitcamp.myapp.dao;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class StudentDao {
/* 아래 코드 수정 */
public void save(String filename) {
try (FileWriter out = new FileWriter(filename)) {
list.forEach(obj -> {
try {
out.write(String.format("%d,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%b,%s,%d\n",
obj.getNo(),
obj.getName(),
obj.getTel(),
obj.getCreatedDate(),
obj.getPostNo(),
obj.getBasicAddress(),
obj.getDetailAddress(),
obj.isWorking(),
obj.getGender(),
obj.getLevel()));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("데이터 출력 중 오류 발생!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void load(String filename) {
if (list.size() > 0) { // 중복 로딩 방지!
return;
}
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))) {
while (true) {
String str = in.readLine();
if (str == null) {
break;
}
String[] values = str.split(",");
Student obj = new Student();
obj.setNo(Integer.parseInt(values[0]));
obj.setName(values[1]);
obj.setTel(values[2]);
obj.setCreatedDate(values[3]);
obj.setPostNo(values[4]);
obj.setBasicAddress(values[5]);
obj.setDetailAddress(values[6]);
obj.setWorking(Boolean.parseBoolean(values[7]));
obj.setGender(values[8].charAt(0));
obj.setLevel(Byte.parseByte(values[9]));
list.add(obj);
}
if (list.size() > 0) {
lastNo = list.get(list.size() - 1).getNo();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Handler 에 있는 파일 명 .csv로 변경한다.
public class BoardHandler {
public void service() {
/* 중략 */
boardDao.load("board.csv");
while (true) {
System.out.printf("[%s]\n", this.title);
System.out.println("1. 등록");
System.out.println("2. 목록");
System.out.println("3. 조회");
System.out.println("4. 변경");
System.out.println("5. 삭제");
System.out.println("6. 검색");
System.out.println("0. 이전");
int menuNo = Prompt.inputInt(String.format("%s> ", this.title));
switch (menuNo) {
case 0:
boardDao.save("board.csv");
return;
case 1: this.inputBoard(); break;
case 2: this.printBoards(); break;
case 3: this.printBoard(); break;
case 4: this.modifyBoard(); break;
case 5: this.deleteBoard(); break;
case 6: this.searchBoard(); break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 메뉴 번호 입니다.");
}
}
}
}
public class TeacherHandler {
/* 중략 */
public void service() {
teacherDao.load("teacher.csv");
while (true) {
System.out.printf("[%s]\n", this.title);
System.out.println("1. 등록");
System.out.println("2. 목록");
System.out.println("3. 조회");
System.out.println("4. 변경");
System.out.println("5. 삭제");
System.out.println("0. 이전");
int menuNo = Prompt.inputInt(String.format("%s> ", this.title));
switch (menuNo) {
case 0:
teacherDao.save("teacher.csv");
return;
case 1: this.inputTeacher(); break;
case 2: this.printTeachers(); break;
case 3: this.printTeacher(); break;
case 4: this.modifyTeacher(); break;
case 5: this.deleteTeacher(); break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 메뉴 번호 입니다.");
}
}
}
}
public class StudentHandler {
public void service() {
/* 중략 */
memberDao.load("student.csv");
while (true) {
System.out.printf("[%s]\n", this.title);
System.out.println("1. 등록");
System.out.println("2. 목록");
System.out.println("3. 조회");
System.out.println("4. 변경");
System.out.println("5. 삭제");
System.out.println("6. 검색");
System.out.println("0. 이전");
int menuNo;
try {
menuNo = Prompt.inputInt(String.format("%s> ", this.title));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("메뉴 번호가 옳지 않습니다.");
continue;
}
try {
switch (menuNo) {
case 0:
memberDao.save("student.csv");
return;
case 1: this.inputMember(); break;
case 2: this.printMembers(); break;
case 3: this.printMember(); break;
case 4: this.modifyMember(); break;
case 5: this.deleteMember(); break;
case 6: this.searchMember(); break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 메뉴 번호 입니다.");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("명령 실행 중 오류 발생! - %s : %s\n",
e.getMessage(),
e.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
}
}
30. 리팩토링 : Information Expert, Factory Method 패턴 적용
### 30. 리팩토링: Factory Method 패턴, Information Expert 패턴
- CSV 데이터를 가지고 Board 객체를 생성하는 일은 Board 클래스에 맡긴다.
- 객체 생성은 메서드를 통해 수행한다. => Factory Method 패턴
- Board 객체의 값을 CSV 형식으로 변환하는 일은 Board 클래스에 맡긴다.
- CSV 데이터 생성은 Board의 메서드를 통해 수행한다. => Information Expert 패턴
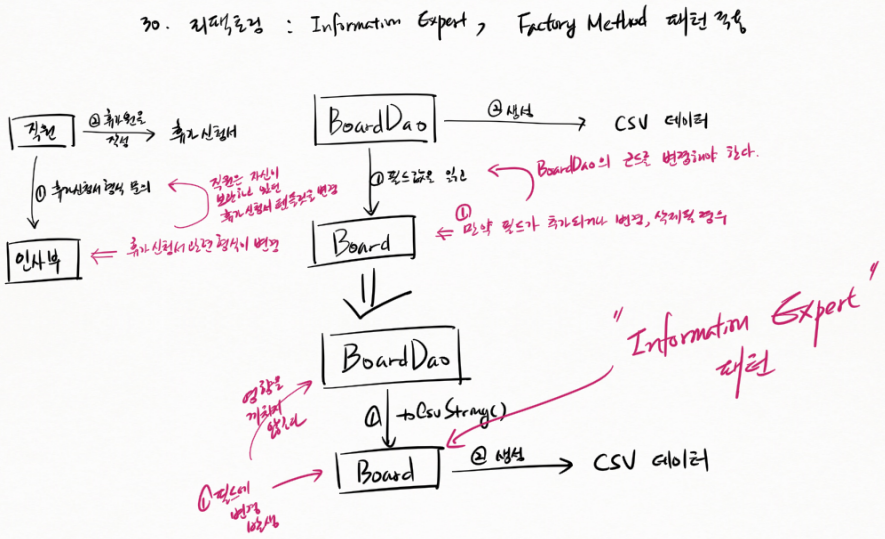
BoardDao 에서 Board의 ① 필드값을 읽고 CSV 데이터를 ② 생성한다.
Board에 ① 만약 필드가 추가되거나 변경, 삭제될 경우 BoardDao 의 코드를 변경해야 한다.
Board에 Information Expert 패턴을 적용해 다음과 같이 변경한다.
BoardDao 에서 ①Board 의 toCsvString() 을 사용한다. Board는 CSV 데이터를 ② 생성한다.
Board ① 필드에 변경 발생해도 BoardDao 에 영향을 끼치지 않는다.
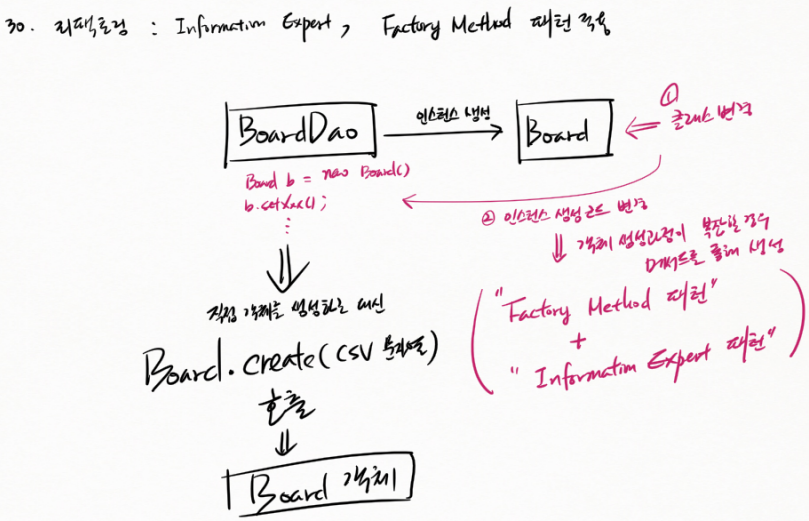
BoardDao 에서 Board 인스턴스 생성 한다. Board 의 ① 클래스 변경이 일어나면 BoardDao의 ② 인스턴스 생성 코드 변경 필요하다. 객체 생성 과정이 복잡할 경우 메서드를 통해 생성한다. ("Factory Method 패턴" + "Information Expert 패턴")
직접 객체를 생성하는 대신 Board.create(csv 문자열) 호출해 Board 객체 생성한다.
public class BoardDao {
public void save(String filename) {
try (FileWriter out = new FileWriter(filename)) {
list.forEach(b -> {
try {
out.write(b.toCsvString() + "\n");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("데이터 출력 중 오류 발생!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void load(String filename) {
if (list.size() > 0) { // 중복 로딩 방지!
return;
}
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))) {
String csv = null;
while ((csv = in.readLine()) != null) {
list.add(Board.create(csv));
}
if (list.size() > 0) {
lastNo = list.get(list.size() - 1).getNo();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public class Board implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private int no;
private String title;
private String content;
private String password;
private String createdDate;
private int viewCount;
// Factory Method 패턴 + Information Expert 패턴
public static Board create(String csv) {
try {
String[] values = csv.split(",");
Board obj = new Board();
obj.setNo(Integer.parseInt(values[0]));
obj.setTitle(values[1]);
obj.setContent(values[2]);
obj.setPassword(values[3]);
obj.setViewCount(Integer.parseInt(values[4]));
obj.setCreatedDate(values[5]);
return obj;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Board 객체 생성 오류!", e);
}
}
// Information Expert 패턴
public String toCsvString() {
return String.format("%d,%s,%s,%s,%d,%s",
this.getNo(),
this.getTitle(),
this.getContent(),
this.getPassword(),
this.getViewCount(),
this.getCreatedDate());
}
public class TeacherDao {
public void save(String filename) {
try (FileWriter out = new FileWriter(filename)) {
list.forEach(obj -> {
try {
out.write(obj.toCsvString() + "\n");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("데이터 출력 중 오류 발생!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void load(String filename) {
if (list.size() > 0) { // 중복 로딩 방지!
return;
}
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))) {
String str = null;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
list.add(Teacher.create(str));
}
if (list.size() > 0) {
lastNo = list.get(list.size() - 1).getNo();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public class Teacher extends Member implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String email;
private int degree;
private String school;
private String major;
private int wage;
// Factory Method 패턴 + Information Expert 패턴
public static Teacher create(String csv) {
try {
String[] values = csv.split(",");
Teacher obj = new Teacher();
obj.setNo(Integer.parseInt(values[0]));
obj.setName(values[1]);
obj.setTel(values[2]);
obj.setCreatedDate(values[3]);
obj.setEmail(values[4]);
obj.setDegree(Integer.parseInt(values[5]));
obj.setSchool(values[6]);
obj.setMajor(values[7]);
obj.setWage(Integer.parseInt(values[8]));
return obj;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Board 객체 생성 오류!", e);
}
}
// Information Expert 패턴
public String toCsvString() {
return String.format("%d,%s,%s,%s,%s,%d,%s,%s,%d",
this.getNo(),
this.getName(),
this.getTel(),
this.getCreatedDate(),
this.getEmail(),
this.getDegree(),
this.getSchool(),
this.getMajor(),
this.getWage());
}
public class StudentDao {
public void save(String filename) {
try (FileWriter out = new FileWriter(filename)) {
list.forEach(obj -> {
try {
out.write(obj.toCsvString() + "\n");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("데이터 출력 중 오류 발생!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void load(String filename) {
if (list.size() > 0) { // 중복 로딩 방지!
return;
}
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))) {
String str = null;
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
list.add(Student.create(str));
}
if (list.size() > 0) {
lastNo = list.get(list.size() - 1).getNo();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public class Student extends Member implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String postNo;
private String basicAddress;
private String detailAddress;
private boolean working;
private char gender;
private byte level;
// Factory Method 패턴 + Information Expert 패턴
public static Student create(String csv) {
try {
String[] values = csv.split(",");
Student obj = new Student();
obj.setNo(Integer.parseInt(values[0]));
obj.setName(values[1]);
obj.setTel(values[2]);
obj.setCreatedDate(values[3]);
obj.setPostNo(values[4]);
obj.setBasicAddress(values[5]);
obj.setDetailAddress(values[6]);
obj.setWorking(Boolean.parseBoolean(values[7]));
obj.setGender(values[8].charAt(0));
obj.setLevel(Byte.parseByte(values[9]));
return obj;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Board 객체 생성 오류!", e);
}
}
// Information Expert 패턴
public String toCsvString() {
return String.format("%d,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%s,%b,%s,%d",
this.getNo(),
this.getName(),
this.getTel(),
this.getCreatedDate(),
this.getPostNo(),
this.getBasicAddress(),
this.getDetailAddress(),
this.isWorking(),
this.getGender(),
this.getLevel());
}
31. JSON 형식으로 데이터 입출력
### 31. JSON 형식으로 데이터 입출력하기: Gson 라이브러리 사용
- JSON 형식으로 데이터를 읽고 쓰는 법
- Google 에서 제공해주는 JSON 라이브러리인 Gson 사용법

객체를 Gson 의 toJson() 이용해 json 파일로 변환한다. FileWriter 의 write() 로 JSON 형식의 문자열로 변환한다. 그러면 JSON 텍스트를 텍스트 파일로 변환시킨다.
텍스트 파일을 JSON 텍스트로 변환하기 위해 FileReader 의 read() 사용한다. Gson 의 fromJson() 이용해 객체로 변환한다.
Gson 라이브러리 추가
https://search.maven.org/ 에서 들어가 gson 검색해서 google 것 선택한다.
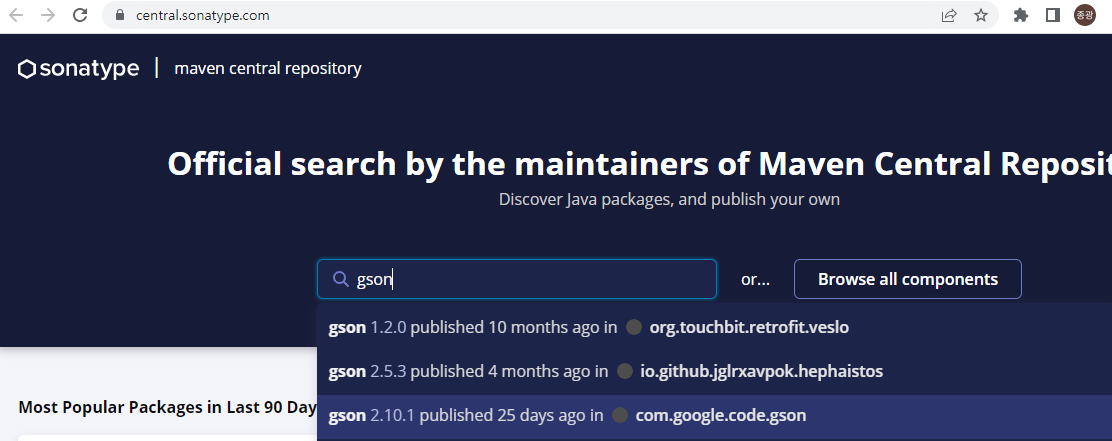
2.10.1 버전 선택하고 Gradle (short) 선택해서 나오는 코드 복사한다.
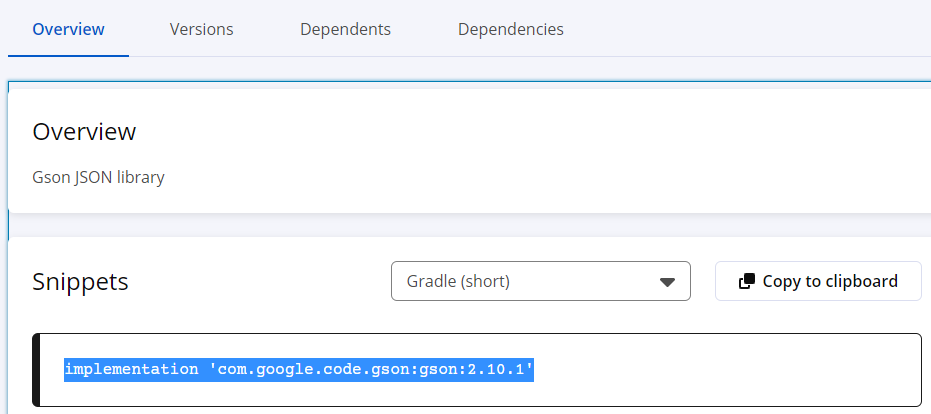
build.gradle > dependencies 에 코드 추가한다.
명령 프롬프트에서 아래 입력해 적용한다.
C:\Users\bitcamp\git\bitcamp-ncp\myapp>gradle eclipse
package bitcamp.myapp.dao;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.common.reflect.TypeToken;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import bitcamp.myapp.vo.Board;
public class BoardDao {
public void save(String filename) {
try (FileWriter out = new FileWriter(filename)) {
out.write(new Gson().toJson(list));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void load(String filename) {
if (list.size() > 0) { // 중복 로딩 방지!
return;
}
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))) {
// 1) JSON 데이터를 어떤 타입의 객체로 변환할 것인지 그 타입 정보를 준비한다.
TypeToken<List<Board>> collectionType = new TypeToken<>() {};
// 2) 입력 스트림에서 JSON 데이터를 읽고, 지정한 타입의 객체로 변환하여 리턴한다.
list = new Gson().fromJson(in, (Type) collectionType);
if (list.size() > 0) {
lastNo = list.get(list.size() - 1).getNo();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package bitcamp.myapp.dao;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import bitcamp.myapp.vo.Teacher;
public class TeacherDao {
/* 아래 코드 수정 */
public void save(String filename) {
try (FileWriter out = new FileWriter(filename)) {
out.write(new Gson().toJson(list));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void load(String filename) {
if (list.size() > 0) { // 중복 로딩 방지!
return;
}
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))) {
list = new Gson().fromJson(in, new TypeToken<List<Teacher>>() {});
if (list.size() > 0) {
lastNo = list.get(list.size() - 1).getNo();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package bitcamp.myapp.dao;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import bitcamp.myapp.vo.Student;
public class StudentDao {
public void save(String filename) {
try (FileWriter out = new FileWriter(filename)) {
out.write(new Gson().toJson(list));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void load(String filename) {
if (list.size() > 0) { // 중복 로딩 방지!
return;
}
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename))) {
list = new Gson().fromJson(in, new TypeToken<List<Student>>() {});
if (list.size() > 0) {
lastNo = list.get(list.size() - 1).getNo();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Handler 에 있는 파일 명 .json으로 변경한다.
public class BoardHandler {
public void service() {
/* 중략 */
boardDao.load("board.json");
while (true) {
System.out.printf("[%s]\n", this.title);
System.out.println("1. 등록");
System.out.println("2. 목록");
System.out.println("3. 조회");
System.out.println("4. 변경");
System.out.println("5. 삭제");
System.out.println("6. 검색");
System.out.println("0. 이전");
int menuNo = Prompt.inputInt(String.format("%s> ", this.title));
switch (menuNo) {
case 0:
boardDao.save("board.json");
return;
case 1: this.inputBoard(); break;
case 2: this.printBoards(); break;
case 3: this.printBoard(); break;
case 4: this.modifyBoard(); break;
case 5: this.deleteBoard(); break;
case 6: this.searchBoard(); break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 메뉴 번호 입니다.");
}
}
}
}
public class TeacherHandler {
/* 중략 */
public void service() {
teacherDao.load("teacher.json");
while (true) {
System.out.printf("[%s]\n", this.title);
System.out.println("1. 등록");
System.out.println("2. 목록");
System.out.println("3. 조회");
System.out.println("4. 변경");
System.out.println("5. 삭제");
System.out.println("0. 이전");
int menuNo = Prompt.inputInt(String.format("%s> ", this.title));
switch (menuNo) {
case 0:
teacherDao.save("teacher.json");
return;
case 1: this.inputTeacher(); break;
case 2: this.printTeachers(); break;
case 3: this.printTeacher(); break;
case 4: this.modifyTeacher(); break;
case 5: this.deleteTeacher(); break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 메뉴 번호 입니다.");
}
}
}
}
public class StudentHandler {
public void service() {
/* 중략 */
memberDao.load("student.json");
while (true) {
System.out.printf("[%s]\n", this.title);
System.out.println("1. 등록");
System.out.println("2. 목록");
System.out.println("3. 조회");
System.out.println("4. 변경");
System.out.println("5. 삭제");
System.out.println("6. 검색");
System.out.println("0. 이전");
int menuNo;
try {
menuNo = Prompt.inputInt(String.format("%s> ", this.title));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("메뉴 번호가 옳지 않습니다.");
continue;
}
try {
switch (menuNo) {
case 0:
memberDao.save("student.json");
return;
case 1: this.inputMember(); break;
case 2: this.printMembers(); break;
case 3: this.printMember(); break;
case 4: this.modifyMember(); break;
case 5: this.deleteMember(); break;
case 6: this.searchMember(); break;
default:
System.out.println("잘못된 메뉴 번호 입니다.");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf("명령 실행 중 오류 발생! - %s : %s\n",
e.getMessage(),
e.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
}
}
예제 소스
gson 라이브러리 추가
build.gradle 의 dependencies 에 아래 추가한다.
// Google JSON 라이브러리
implementation 'com.google.code.gson:gson:2.10.1'
// jackson-databind JSON 라이브러리
implementation 'com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-databind:2.14.2'
위 코드 출처는 아래 사이트이다.
json.org 사이트에 언어별 json 라이브러리 정보 있다.
com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson
JSON 라이브러리 준비 - Gson 라이브러러 가져오기
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0100 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Gson 라이브러리를 프로젝트에 추가한다.
// 1) `build.gradle` 빌드 스크립트 파일 변경
// - Gson 라이브러리 정보를 dependecies {} 블록에 추가한다.
// - https://search.maven.org/ 사이트에 방문한다.
// - `gson` 검색어로 라이브러리를 찾는다.
// - `com.google.code.gson` 라이브러리를 선택한다.
// - 검색 결과에서 최신 버전을 선택한다.
// - Gradle Groovy DSL 코드를 복사하여 빌드 스크립트에 붙여 넣는다.
// 2) `$ gradle eclipse` 를 실행하여 라이브러리를 다운로드하여 프로젝트에 등록한다.
// - 명령을 실행한 후 eclipse IDE 에서 해당 프로젝트를 refresh 해야 한다.
// - 'Referenced Libraries' 노드에서 gson 라이브러리 파일이 추가된 것을 확인한다.
Gson gson = new Gson();
}
}
객체 --> JSON 문자열 : 객체의 필드 값을 json 형식의 문자열로 만들기
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.sql.Date;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0110 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1) 객체 준비
Member m = new Member();
m.setNo(100);
m.setName("홍길동");
m.setEmail("hong@test.com");
m.setPassword("1111");
m.setPhoto("hong.gif");
m.setTel("010-2222-1111");
m.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
// 2) JSON 처리 객체 준비
Gson gson = new Gson();
// 3) 객체의 값을 JSON 문자열로 얻기
String jsonStr = gson.toJson(m);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
}
}
// JSON 객체 형식 - { 객체 정보 }
// => { "프로퍼티명" : 값, "프로퍼티명": 값, ...}
//
// 값:
// - 문자열 => "값"
// - 숫자 => 값
// - 논리 => true, false
//
// 프로퍼티명은 반드시 문자열로 표현해야 한다.
JSON 문자열 --> 객체 : JSON 문자열을 해석하여 객체를 생성하기
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0120 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1) JSON 문자열 준비
String jsonStr = "{\"no\":100,\"name\":\"홍길동\",\"email\":\"hong@test.com\",\"password\":\"1111\",\"photo\":\"hong.gif\",\"tel\":\"010-2222-1111\",\"registeredDate\":\"1월 24, 2022\"}";
// 2) JSON 처리 객체 준비
Gson gson = new Gson();
// 3) JSON 문자열을 가지고 객체 만들기
Member m = gson.fromJson(jsonStr, Member.class);
System.out.println(m);
}
}
JSON 문자열 --> 객체 : JSON 문자열에는 클래스 정보가 없다.
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0130 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1) JSON 문자열 준비
String jsonStr = "{\"no\":100,\"name\":\"홍길동\",\"email\":\"hong@test.com\",\"password\":\"1111\",\"photo\":\"hong.gif\",\"tel\":\"010-2222-1111\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"}";
// 2) JSON 처리 객체 준비
Gson gson = new Gson();
// 3) JSON 문자열을 가지고 객체 만들기
// - JSON 문자열에서 프로퍼티 이름과 일치하는 필드가 객체에 있다면 값을 설정해 준다.
// - 예)
// JSON 문자열 ------> Board 객체
// no no
// name X
// email X
// password X
// photo X
// tel X
// registeredDate registeredDate
//
Board b = gson.fromJson(jsonStr, Board.class);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
객체 --> JSON 문자열 : 배열 다루기
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.sql.Date;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0210 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1) 배열 준비
Member m1 = new Member();
m1.setNo(101);
m1.setName("홍길동");
m1.setEmail("hong@test.com");
m1.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Member m2 = new Member();
m2.setNo(102);
m2.setName("임꺽정");
m2.setEmail("leem@test.com");
m2.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Member m3 = new Member();
m3.setNo(103);
m3.setName("안창호");
m3.setEmail("ahn@test.com");
m3.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Member[] members = {m1, m2, m3};
String jsonStr = new Gson().toJson(members);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
}
}
// JSON 배열 형식 - [{ 객체 정보 },{ 객체 정보}, ...]
// => [
// {"프로퍼티명":값,"프로퍼티명":값, ...},
// {"프로퍼티명":값,"프로퍼티명":값, ...},
// {"프로퍼티명":값,"프로퍼티명":값, ...},
// ...
// ]
JSON 문자열 --> 객체 : 배열 다루기
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0220 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "[{\"no\":101,\"name\":\"홍길동\"},{\"no\":102,\"name\":\"임꺽정\"},{\"no\":103,\"name\":\"안창호\"}]";
Member[] members = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr, Member[].class);
for (Member m : members) {
System.out.println(m);
}
}
}
객체 --> JSON 문자열 : 컬렉션 다루기
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0310 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1) ArrayList 준비
Member m1 = new Member();
m1.setNo(101);
m1.setName("홍길동");
m1.setEmail("hong@test.com");
m1.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Member m2 = new Member();
m2.setNo(102);
m2.setName("임꺽정");
m2.setEmail("leem@test.com");
m2.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Member m3 = new Member();
m3.setNo(103);
m3.setName("안창호");
m3.setEmail("ahn@test.com");
m3.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
ArrayList<Member> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(m1);
list.add(m2);
list.add(m3);
String jsonStr = new Gson().toJson(list);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
}
}
// JSON 컬렉션 형식 - [{ 객체 정보 },{ 객체 정보}, ...]
// => 배열을 출력한 것과 같다.
// JSON은 배열과 컬렉션을 구분하지 않는다.
// => [
// {"프로퍼티명":값,"프로퍼티명":값, ...},
// {"프로퍼티명":값,"프로퍼티명":값, ...},
// {"프로퍼티명":값,"프로퍼티명":값, ...},
// ...
// ]
JSON 문자열 --> 객체 : 컬렉션 다루기
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.Collection;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
public class Exam0320 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "[{\"no\":101,\"name\":\"홍길동\"},{\"no\":102,\"name\":\"임꺽정\"},{\"no\":103,\"name\":\"안창호\"}]";
// 1) TypeToken 클래스의 서브 클래스를 만든다.
class MyTypeToken extends TypeToken<Collection<Member>> {
// 수퍼 클래스를 지정할 때 제네릭의 타입을 설정한다.
// TypeToken 클래스에는 Type 인터페이스의 구현체를 만드는 메서드가 있기 때문에
// 이 클래스의 서브 클래스를 만드는 것이다.
// 타입 파라미터에 컬렉션 타입을 전달하는 목적 이외에는 다른 이유가 없다.
// 그래서 서브 클래스에 뭔가를 추가할 필요가 없다.
}
// 2) TypeToken 객체 준비
MyTypeToken typeToken = new MyTypeToken();
// 3) TypeToken 객체를 통해 Type 구현체를 얻는다.
Type collectionType = typeToken.getType();
// 4) Type 객체에 저장된 정보를 바탕으로 JSON 문자열로부터 컬렉션 객체를 만든다.
Collection<Member> list = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr, collectionType);
for (Member m : list) {
System.out.println(m);
}
}
}
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.Collection;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
public class Exam0321 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "[{\"no\":101,\"name\":\"홍길동\"},{\"no\":102,\"name\":\"임꺽정\"},{\"no\":103,\"name\":\"안창호\"}]";
// Exam0320의 코드를 익명 클래스를 이용하여 간결하게 정리한 것이다.
Type collectionType = new TypeToken<Collection<Member>>(){}.getType();
Collection<Member> list = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr, collectionType);
for (Member m : list) {
System.out.println(m);
}
}
}
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.Collection;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
public class Exam0322 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "[{\"no\":101,\"name\":\"홍길동\"},{\"no\":102,\"name\":\"임꺽정\"},{\"no\":103,\"name\":\"안창호\"}]";
// Exam0321과 다른 방법으로 Type 객체를 얻기
Type collectionType = TypeToken.getParameterized(Collection.class, Member.class).getType();
Collection<Member> list = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr, collectionType);
for (Member m : list) {
System.out.println(m);
}
}
}
객체 --> JSON 문자열 : 다른 객체를 포함하는 경우
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.sql.Date;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0410 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1) 객체 준비
Member m = new Member();
m.setNo(100);
m.setName("홍길동");
m.setEmail("hong@test.com");
m.setPassword("1111");
m.setPhoto("hong.gif");
m.setTel("010-2222-1111");
m.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Board b = new Board();
b.setNo(1);
b.setTitle("제목");
b.setContent("내용");
b.setWriter(m);
b.setViewCount(98);
b.setLike(5);
b.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
String jsonStr = new Gson().toJson(b);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
}
}
// 다른 객체를 포함했을 때 JSON 형식
// {
// 프로퍼티명 : 값,
// 프로퍼티명 : {프로퍼티명:값,프로퍼티명:값,...},
// ...
// }
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0420 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "{\"no\":1,\"title\":\"제목\",\"content\":\"내용\",\"writer\":{\"no\":100,\"name\":\"홍길동\",\"email\":\"hong@test.com\",\"password\":\"1111\",\"photo\":\"hong.gif\",\"tel\":\"010-2222-1111\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"},\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\",\"viewCount\":98,\"like\":5}";
Board b = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr, Board.class);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
객체 --> JSON 문자열 : 다른 객체를 목록으로 포함하는 경우
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0510 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1) 객체 준비
Member m1 = new Member();
m1.setNo(101);
m1.setName("홍길동");
m1.setEmail("hong@test.com");
m1.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Member m2 = new Member();
m2.setNo(102);
m2.setName("임꺽정");
m2.setEmail("leem@test.com");
m2.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Member m3 = new Member();
m3.setNo(103);
m3.setName("안창호");
m3.setEmail("ahn@test.com");
m3.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
ArrayList<Member> members = new ArrayList<>();
members.add(m1);
members.add(m2);
members.add(m3);
Project p = new Project();
p.setNo(11);
p.setTitle("제목");
p.setContent("내용");
p.setStartDate(Date.valueOf("2021-1-1"));
p.setEndDate(Date.valueOf("2021-2-2"));
p.setOwner(m2);
p.setMembers(members);
String jsonStr = new Gson().toJson(p);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
}
}
// 다른 객체를 목록으로 포함했을 때 JSON 형식
// {
// 프로퍼티명 : 값,
// 프로퍼티명 : {프로퍼티명:값,프로퍼티명:값,...},
// 프로퍼티명 : [{...},{...},{...},...],
// ...
// }
JSON 문자열 --> 객체 : 다른 객체를 여러 개 포함하는 경우
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0520 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "{\"no\":11,\"title\":\"제목\",\"content\":\"내용\",\"startDate\":\"1월 1, 2021\",\"endDate\":\"2월 2, 2021\",\"owner\":{\"no\":102,\"name\":\"임꺽정\",\"email\":\"leem@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"},\"members\":[{\"no\":101,\"name\":\"홍길동\",\"email\":\"hong@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"},{\"no\":102,\"name\":\"임꺽정\",\"email\":\"leem@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"},{\"no\":103,\"name\":\"안창호\",\"email\":\"ahn@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"}],\"tasks\":[]}";
Project p = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr, Project.class);
System.out.println(p);
}
}
객체 --> JSON 문자열 : 다양한 타입의 객체를 목록에 포함하는 경우
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0610 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1) 객체 준비
Manager mgr = new Manager();
mgr.setNo(101);
mgr.setName("홍길동");
mgr.setEmail("hong@test.com");
mgr.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
mgr.setPosition("대리");
mgr.setFax("02-1111-2222");
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
teacher.setNo(103);
teacher.setName("안창호");
teacher.setEmail("ahn@test.com");
teacher.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
teacher.setMajor("컴퓨터공학");
teacher.setHourPay(10000);
ArrayList<Member> members = new ArrayList<>();
members.add(mgr);
members.add(teacher);
String jsonStr = new Gson().toJson(members);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
}
}
JSON 문자열 --> 객체 : 다른 객체를 여러 개 포함하는 경우
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.Collection;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
public class Exam0620 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "[{\"position\":\"대리\",\"fax\":\"02-1111-2222\",\"no\":101,\"name\":\"홍길동\",\"email\":\"hong@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"},{\"major\":\"컴퓨터공학\",\"hourPay\":10000,\"no\":103,\"name\":\"안창호\",\"email\":\"ahn@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"}]";
Type collectionType = TypeToken.getParameterized(Collection.class, Member.class).getType();
Collection<Member> list = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr, collectionType);
for (Member m : list) {
System.out.println(m);
}
}
}
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.Collection;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
import com.google.gson.JsonDeserializationContext;
import com.google.gson.JsonDeserializer;
import com.google.gson.JsonElement;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import com.google.gson.JsonParseException;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
public class Exam0621 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "[{\"position\":\"대리\",\"fax\":\"02-1111-2222\",\"no\":101,\"name\":\"홍길동\",\"email\":\"hong@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"},{\"major\":\"컴퓨터공학\",\"hourPay\":10000,\"no\":103,\"name\":\"안창호\",\"email\":\"ahn@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"}]";
// JSON 데이터를 가지고 객체를 생성할 때 특정 타입의 객체로 만들어주는 어댑터
// => 프로퍼티의 존재 유무에 따라 Manager를 생성하든가 Teacher를 생성하는 일을 한다.
class MyJsonDeserializer implements JsonDeserializer<Member> {
@Override
public Member deserialize(JsonElement json, Type typeOfT,
JsonDeserializationContext context) throws JsonParseException {
JsonObject jsonObject = json.getAsJsonObject();
if (jsonObject.get("position") != null) {
return context.deserialize(jsonObject, Manager.class);
} else {
return context.deserialize(jsonObject, Teacher.class);
}
}
}
// Gson 객체를 만들어주는 공장
GsonBuilder gsonBuilder = new GsonBuilder();
// 공장에 객체 생성기(JsonDeserializer)를 꼽는다.
gsonBuilder.registerTypeAdapter(Member.class, new MyJsonDeserializer());
// 공장을 통해 Gson 객체를 준비한다.
Gson gson = gsonBuilder.create();
// Gson 객체가 JSON 데이터를 가지고 객체를 생성할 때 알아야 하는 객체 타입 정보 준비
Type collectionType = TypeToken.getParameterized(Collection.class, Member.class).getType();
// JSON 데이터를 읽어서 주어진 타입의 객체를 생성한다.
// => 단 내부에 설정된 객체 어댑터(JsonDeserializer)를 이용하여 객체를 생성한다.
Collection<Member> list = gson.fromJson(jsonStr, collectionType);
for (Member m : list) {
System.out.println(m);
}
}
}
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.Collection;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
import com.google.gson.JsonDeserializationContext;
import com.google.gson.JsonDeserializer;
import com.google.gson.JsonElement;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import com.google.gson.JsonParseException;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
public class Exam0622 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "[{\"position\":\"대리\",\"fax\":\"02-1111-2222\",\"no\":101,\"name\":\"홍길동\",\"email\":\"hong@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"},{\"major\":\"컴퓨터공학\",\"hourPay\":10000,\"no\":103,\"name\":\"안창호\",\"email\":\"ahn@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"9월 16, 2021\"}]";
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder()
.registerTypeAdapter(Member.class, new JsonDeserializer<Member>() {
@Override
public Member deserialize(JsonElement json, Type typeOfT,
JsonDeserializationContext context) throws JsonParseException {
JsonObject jsonObject = json.getAsJsonObject();
if (jsonObject.get("position") != null) {
return context.deserialize(jsonObject, Manager.class);
} else {
return context.deserialize(jsonObject, Teacher.class);
}
}
})
.create();
Type collectionType = TypeToken.getParameterized(Collection.class, Member.class).getType();
Collection<Member> list = gson.fromJson(jsonStr, collectionType);
for (Member m : list) {
System.out.println(m);
}
}
}
맵객체 --> JSON 문자열
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0710 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 자바 기본 타입과 객체를 묶어서 JSON으로 내보내기
Manager mgr = new Manager();
mgr.setNo(101);
mgr.setName("홍길동");
mgr.setEmail("hong@test.com");
mgr.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
mgr.setPosition("대리");
mgr.setFax("02-1111-2222");
HashMap<String,Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("no", String.valueOf(100));
params.put("title", "Hello");
params.put("manager", mgr);
String jsonStr = new Gson().toJson(params);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
}
}
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0711 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 자바 기본 타입과 객체를 묶어서 JSON으로 내보내기
Manager mgr = new Manager();
mgr.setNo(101);
mgr.setName("홍길동");
mgr.setEmail("hong@test.com");
mgr.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
mgr.setPosition("대리");
mgr.setFax("02-1111-2222");
HashMap<String,String> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("no", String.valueOf(100));
params.put("title", "Hello");
params.put("manager", new Gson().toJson(mgr));
String jsonStr = new Gson().toJson(params);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
}
}
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.sql.Date;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0712 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 자바 기본 타입과 객체를 묶어서 JSON으로 내보내기
Manager mgr = new Manager();
mgr.setNo(101);
mgr.setName("홍길동");
mgr.setEmail("hong@test.com");
mgr.setRegisteredDate(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
mgr.setPosition("대리");
mgr.setFax("02-1111-2222");
ManagerParam param = new ManagerParam();
param.no = 100;
param.title = "Hello";
param.manager = mgr;
String jsonStr = new Gson().toJson(param);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
}
}
JSON 문자열 --> 객체 : 다른 객체를 여러 개 포함하는 경우
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.util.Map;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0720 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "{\"no\":\"100\",\"manager\":{\"position\":\"대리\",\"fax\":\"02-1111-2222\",\"no\":101,\"name\":\"홍길동\",\"email\":\"hong@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"10월 5, 2021\"},\"title\":\"Hello\"}";
Map<String,Object> map = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr, Map.class);
Object v1 = map.get("no");
Object v2 = map.get("title");
Object v3 = map.get("manager");
System.out.println(v1.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(v2.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(v3.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(map.get("no"));
System.out.println(map.get("title"));
System.out.println(map.get("manager"));
}
}
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import java.util.Map;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0721 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "{\"no\":\"100\",\"manager\":\"{\\\"position\\\":\\\"대리\\\",\\\"fax\\\":\\\"02-1111-2222\\\",\\\"no\\\":101,\\\"name\\\":\\\"홍길동\\\",\\\"email\\\":\\\"hong@test.com\\\",\\\"registeredDate\\\":\\\"10월 5, 2021\\\"}\",\"title\":\"Hello\"}";
Map<String,String> map = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr, Map.class);
String v1 = map.get("no");
String v2 = map.get("title");
String v3 = map.get("manager");
System.out.println(v1);
System.out.println(v2);
System.out.println(v3);
Manager mgr = new Gson().fromJson(v3, Manager.class);
System.out.println(mgr);
}
}
package com.eomcs.openapi.json.gson;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Exam0722 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonStr = "{\"no\":100,\"title\":\"Hello\",\"manager\":{\"position\":\"대리\",\"fax\":\"02-1111-2222\",\"no\":101,\"name\":\"홍길동\",\"email\":\"hong@test.com\",\"registeredDate\":\"10월 5, 2021\"}}";
ManagerParam param = new Gson().fromJson(jsonStr, ManagerParam.class);
System.out.println(param.no);
System.out.println(param.title);
System.out.println(param.manager);
}
}
32. 데이터 처리를 별도의 Application 으로 분리
### 32. 네트워킹을 이용한 파일 공유: client/server app. 아키텍처로 전환
- 네트워크를 통해 파일을 공유하고 데이터 입출력을 처리하는 방법
- 데이터를 파일에 저장하고 꺼내는 기능을 별도의 애플리케이션으로 분리한다.
- 기존의 프로그램은 네트워크를 통해 파일 서버에 접속하여 데이터 입출력을 처리한다.
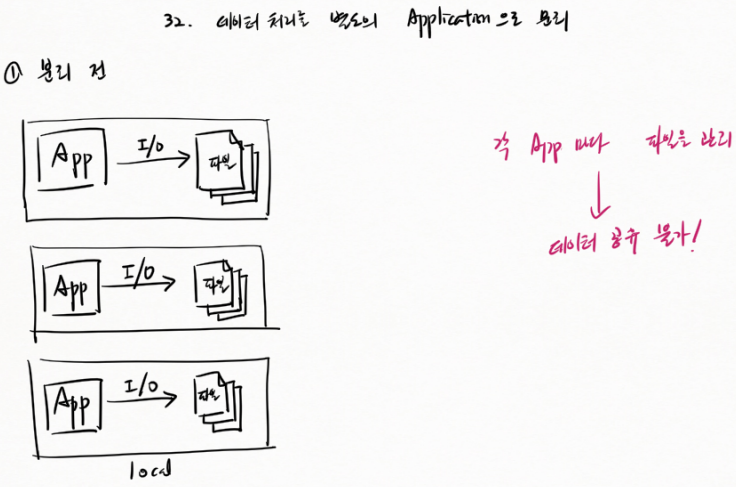
① 분리 전
각 App 에서 I/O 이용해 파일로 출력한다.
각 App 마다 파일을 관리 → 데이터 공유 불가!
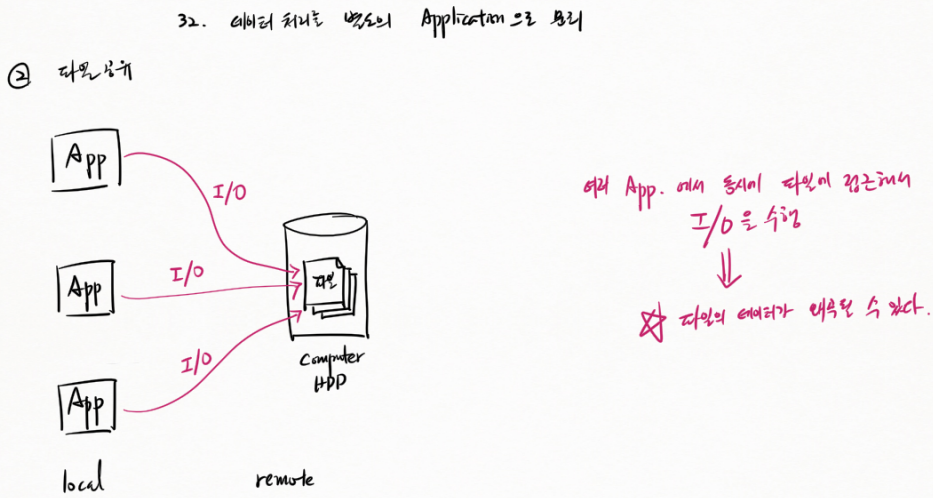
② 파일 공유
local App 에서 remote Computer HDD 에 I/O 로 파일 출력한다.
여러 App. 에서 동시에 파일에 접근해서 I/O 을 수행 → 파일의 데이터가 왜곡될 수 있다.

③ 파일 I/O 관리자 도입
local "Client Application" 의 App 에서 remote "Server Application" 의 App 으로 요청하고, App 은 파일로 I/O 한 뒤 응답한다.
원격의 App 이 파일 관리하면 여러 App 의 접근을 제어해서 파일의 데이터 왜곡을 방지한다.
Networking
Client / Server
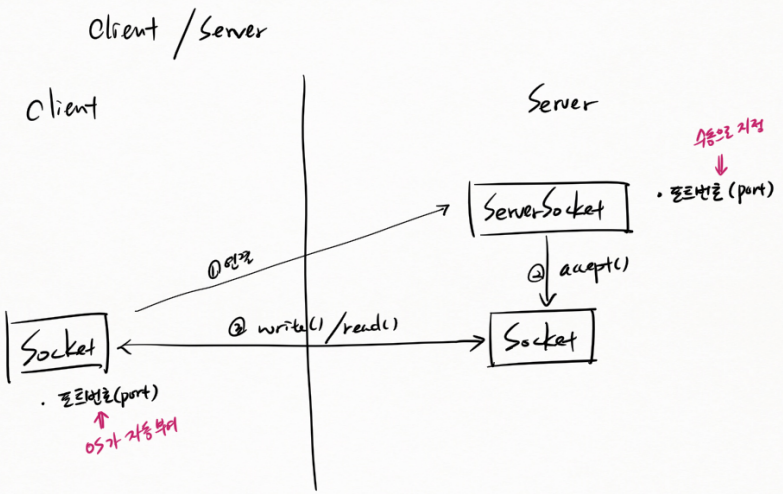
Client 에서 Socket 생성한다. 포트번호(port) 는 OS 가 자동 부여한다. ServerSocket 을 생성하는데 포트번호(port) 는 수동으로 지정한다. client에서 server로 ① 연결한다. 그러면 ② accept() 가 실행되고 Socket 에 객체 저장한다. Socket 끼리 ③ write() / read() 할 수 있다.
cmd에서 서버 실행한다.
C:\Users\bitcamp\git\bitcamp-ncp\eomcs-java-lang\app>java -cp bin/main com.eomcs.net.ServerApp
전송시 한글 깨지면 서버 실행시 다음과 같이 -Dfile.encoding 지정한다.
C:\Users\bitcamp\git\bitcamp-ncp\eomcs-java-lang\app>java -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -cp bin/main com.eomcs.net.ServerApp
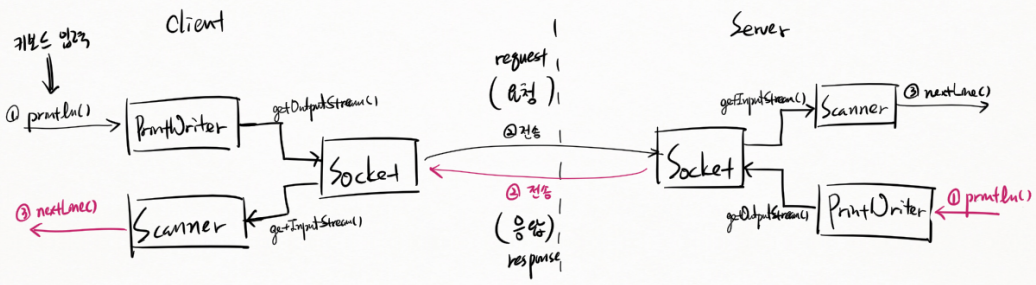
Client 에서 PrintWriter 객체의 ① println() 매개변수에 키보드 입력 받는다. Socket 객체의 getOutputStream() 사용해 ② 전송 (요청, request) 한다.
Server 에서 Socket 객체의 getInputStream() 사용해 데이터 받고 Scanner 의 ③ nextLine() 사용해 읽어들인다.
Server 에서 PrintWriter 객체의 ① println() 사용해 출력하고 Socket 객체의 getOutputStream() 사용해 ② 전송 (응답, response) 한다.
Client 에서 Socket 객체의 getInputStream() 사용해 데이터 받고 Scanner 의 ③ nextLine() 사용해 읽어들인다.
텍스트 주고 받기
package com.eomcs.net;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ServerApp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner keyScan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("서버 실행 중...");
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("클라이언트와 연결됨!");
Scanner in = new Scanner(socket.getInputStream());
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream());
while (true) {
// 클라이언트가 보낸 문자열을 한 줄 읽을 때까지 리턴하지 않는다.
String message = in.nextLine();
System.out.println(message);
if (message.equals("quit")) {
break;
}
System.out.print("입력> ");
String str = keyScan.nextLine();
out.println(str);
}
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
System.out.println("서버 종료!");
keyScan.close();
}
}
package com.eomcs.net;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ClientApp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner keyScan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("클라이언트 실행 중...");
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
System.out.println("서버에 연결되었음!");
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream());
Scanner in = new Scanner(socket.getInputStream());
while (true) {
System.out.print("입력> ");
String message = keyScan.nextLine();
out.println(message);
if (message.equals("quit")) {
break;
}
// System.out.println("서버에 메시지를 보냈음!");
// 서버에서 응답이 올 때까지 리턴하지 않는다.
String response = in.nextLine();
System.out.printf("응답: %s\n", response);
}
out.close();
in.close();
socket.close();
System.out.println("클라이언트 종료!");
keyScan.close();
}
}
파일 주고 받기
package com.eomcs.net;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ServerApp2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("서버 실행 중...");
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("클라이언트와 연결됨!");
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
// 클라이언트가 보낸 파일의 이름을 읽는다.
String filename = in.readUTF();
// 클라이언트가 보낸 파일의 크기를 읽는다.
long length = in.readLong();
// 클라이언트가 보낸 사진 바이트를 파일로 출력한다.
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream(filename);
for (long i = 0; i < length; i++) {
fileOut.write(in.read());
}
fileOut.close();
// 클라이언트에게 응답한다.
out.writeUTF("완료!");
in.close();
out.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
System.out.println("서버 종료!");
}
}
package com.eomcs.net;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ClientApp2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
System.out.println("서버에 연결되었음!");
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
File file = new File("rubberDuck.jpg");
// 전송할 파일의 이름을 보낸다.
out.writeUTF(file.getName());
// 전송할 파일의 크기를 먼저 보낸다.
out.writeLong(file.length());
// 파일을 1바이트씩 읽어 보낸다.
FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream(file);
int b;
while ((b = fileIn.read()) != -1) {
out.write(b);
}
fileIn.close();
// 서버의 응답을 읽는다.
System.out.println(in.readUTF());
out.close();
in.close();
socket.close();
System.out.println("클라이언트 종료!");
}
}
조언
*코드 라인 수를 줄이려고 하지 말고 직관적으로 보이게 짜라.
*돈 버는 일은 원래 힘들다. 연예인도 영업용 미소, 립서비스 가 있다. 일에서 즐거울 요소를 찾아야 한다.
과제
[네트워킹] 사칙연산 계산기 클라이언트/서버 만들기
내용:
- +, -, *, / 를 수행하는 네트워크 계산기를 만든다.
- 클라이언트를 사용하여 서버 계산기를 실행한다.
- 사용자 UI는 자유롭게 만든다.
과제 제출 조건:
- CalcServer.java, CalcClient.java 소스를 제출한다.
- 기타 보조 클래스를 추가해도 된다.
- 팀원 각자가 팀 프로젝트 파일을 제출할 것
- 제출 내용에 다음과 같이 팀명 및 팀원을 명시할 것
예) 1팀: 홍길동, 임꺽정
제출 마감일:
- 2023-02-02(월요일) 09:00
'네이버클라우드 AIaaS 개발자 양성과정 1기 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 예제 소스 정리 - 네트워킹(Client/Server, 연결 방식) (0) | 2023.02.02 |
|---|---|
| [비트캠프] 62일차(13주차4일) - Java(Client, Server 아키텍처), myapp-32-1~2 (0) | 2023.02.02 |
| [비트캠프] 60일차(13주차2일) - Java(데코레이터, I/O stream), myapp-27~28 (0) | 2023.01.31 |
| [Java] 예제 소스 정리 - 파일 입출력 (0) | 2023.01.30 |
| [비트캠프] 59일차(13주차1일) - Java(컬렉션 API, 파일 입출력), myapp-26 (0) | 2023.01.30 |


